What is IAC? – Infrastructure as Code | Benefits, Tools & Best Practices

If you’ve ever wondered how DevOps manage complex infrastructure without clicking like maniacs and losing their minds, they just write a bit of code. That’s called “Infrastructure as Code“, which can turn the chaotic mess of servers, storage, and networking into something you can manage with scripts.
If you’re looking for some real-world examples, check out ServerMania—a dedicated and cloud hosting provider that’s all about making infrastructure work smarter. We know that wrapping your head around IaC can feel like a lot, so here, we will provide a complete breakdown of benefits, tools, and practices.
Let’s start by asking…
What is Infrastructure as Code?
IaC Infrastructure as Code is the technology used for managing, processing, and provisioning infrastructure with code (machine-readable languages). This eliminates the need for manual processes, allowing you to automate administration’s repetitive tasks and keep things running smooth as butter.
Introduced in 2009 by a DevOps organization called Puppet, Infrastructure as Code became a thing, and it’s the root of a ton of other tools and companies—like Ansible, Chef, you name it.
How Does IaC Work?
IaC can manage infrastructure resources in an organized way by treating the configuration files as a code, making it easy for the version control to make updates and track errors. The IaC configuration files are written in Java or Python and are developed in environments (IDEs) that support coding.
Hence, infrastructure as code tools are ideal for administrators and software developers, streamlining the debugging and tracking process. This provides limitless infrastructure configuration options to manage servers easily.
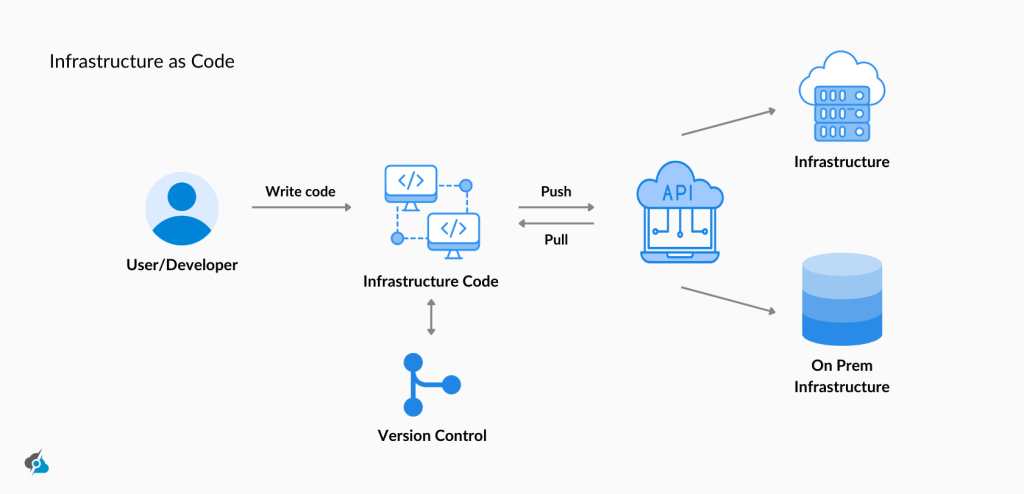
IaC Features
To understand how the provision infrastructure as code works, let’s take a quick look at the main features that make IaC commonly preferred over manual processes and configuration management:
- Automation: IaC handles the setup and configuration of infrastructure automatically, cutting down on human errors and saving valuable time.
- Repeatability: With IaC scripts, you can reuse the same code to build identical infrastructure across different environments without much effort.
- High Security: With infrastructure code, consistent and secure configurations are guaranteed, minimizing the chances of security threats.
- Version Control: The IaC code is saved in a version control system, making it easy to access every version, collaborate with others, and track changes.
- Scalability: The scalability with IaaC is a breeze, considering that adding and removing resources with a code is easy, accessible, and manageable.
- Transparency: With IaC, the infrastructure components are easily understandable since the coding nature clearly defines all relations.
Note: These IaC features don’t just shine in typical IT setups—they can even power niche needs like deploying GPU servers for gaming workloads.
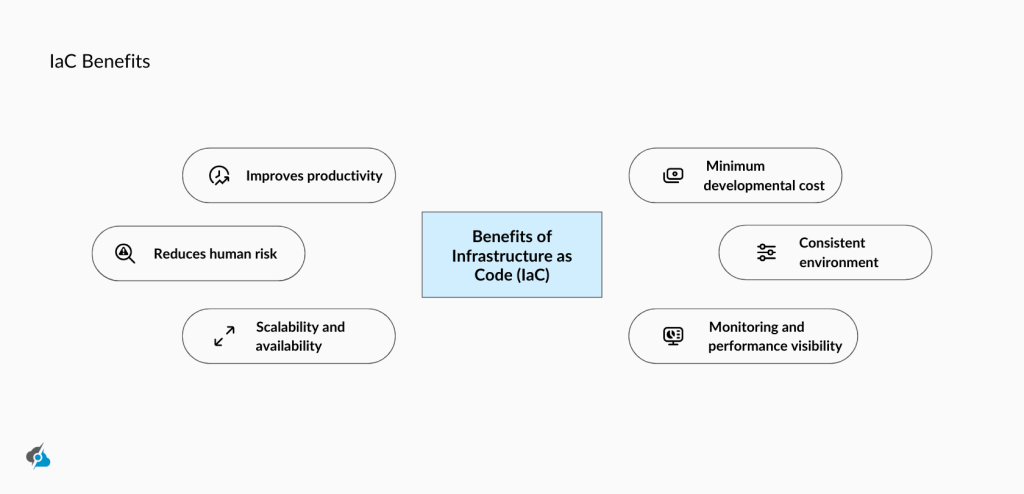
IaC Advantages
Infrastructure as Code IaC comes with a set of advantages that throw away headaches and reperative tasks to deliver simplified automation:
- Fast Deployment: IaC streamlines IT operations and VM configurations to provide software development teams with easy infrastructure and application deployment.
- Better Reliability: IaC enables code changes and delivers consistency, reliability, and repeatability, which reduces manual interaction for infrastructure operations.
- Enhanced Security: The coding framework ensures that the IaC development process is secure and consistent, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Quick Scalability: Infra as code tools break through the old-school immutable infrastructure and deliver an underlying infrastructure that allows quick and easy scalability by adding and removing resources.
- More Collaboration: IaC enables developers to configure infrastructure in the same environment simultaneously, enhancing collaboration, knowledge sharing, and continuous delivery.
IaC Challenges
Although Infrastructure as Code (IaC) comes with many advantages, there are a few major cons that we shouldn’t overlook, so let’s walk you through most of them:
- Setup Time: Implementing IaC effectively takes a lot of time and effort, as it requires writing code, debugging it, and integrating it into an already existing cloud environment.
- Learning: The learning curve when using IaC tools is significant, making it hard for newcomers to adapt quickly, which represents a drawback for organizations without cloud service understanding.
- Fragility: Infrastructure as Code IaC can be fragile, considering the complexity of infrastructure changes where small mistakes matter the most and have a great infrastructure impact.
- Compexity: The IaC framework requires multiple technical components working together to deliver, making it difficult for testing, debugging, and failure identification.
Who Uses Infrastructure Code?
Infrastructure configuration serves a wide range of professionals and organizations, each leveraging its capabilities to streamline their operation teams’ workload.
Whether it’s deploying configuration files for applications, configuring cloud environments, or managing extensive data systems, IaC proves its versatility across various sectors. Let’s explore some of them:
- DevOps: Infrastructure as code services are a critical component of software development, allowing quick deployment of new applications in the production environment and management of existing infrastructure.
- Cloud Providers: Cloud platform providers greatly benefit from IaC solutions used to provision and configure the cloud infrastructure, virtual machines, databases, and storage.
- Network Centers: IaC code tools are used for automating infrastructure components in network management, like creating subnets, firewalls, and security groups.
- Data Centers: Infrastructure Code tools are deployed in the management of large databases by creating tables, configuring users, and specifying the database engine.
Why Choose IaC (Infrastructure Code)
When it comes to infrastructure management, choosing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is like handing your team complete automation. It’s all about forgetting old habits, like manual and repetitive tasks, to adopt a new, more streamlined approach—using code to handle everything.
Companies that adopt IaC find they can manage systems faster and keep everything consistent, which is a big deal, regardless of whether you’re running a small project or an enterprise setup. So, if you need to manage your infrastructure without drowning in manual work, IaC would be the ideal choice for you.
IaC – Infrastructure Management Tools
When it comes to adopting infrastructure as code, many IaC tools stand out, offering ways to automate and streamline everything from basic server configs to complex cloud deployments. As the foundation of Infrastructure as Code IaC, each tool offers unique features to suit different needs.
Let’s check them out:
| Description: | Approach: | Features: | |
| Chef | A configuration management written on Ruby and Erlang for infrastructure automation. | Declarative | Designed for flexibility, Chef supports advanced workflows. |
| Puppet | A configuration management tool designed to automate infrastructure provisioning. | Declarative | Manages centralized configurations and complex setups. |
| Ansible | Easy-to-use, agentless infrastructure management tool used for deployment. | Declarative & Imperative | Leveraging YAML playbooks, Ansible simplifies IT automation. |
| Terraform | Popular open-source tool that supports on-prem and cloud resource dependencies. | Declarative | Modular infrastructure, state management, and extensibility. |
| AWS Cloud Formation | An AWS-enabled management tool automating infrastructure deployment. | Declarative | Integration with the AWS environment with rollback fail-safety capabilities. |
| Kubernetes | An automation platform focused on application deployment and management. | Declarative | Scaling environment, container lifecycle, and networking. |
| SaltStack | Tool for configuration management popular with speed and scalability | Declarative & Imperative | Even-driven, real-time automated testing and security enhanced. |
With these tools in your DevOps team, managing your infrastructure becomes less of a headache and more of an advantage. Each one brings something unique—whether it’s simplifying complex software deployments, boosting scalability, or keeping configurations secure.
Declarative vs Imperative Approach: Types of IaC Practices
When running Infrastructure as Code, you’ll run into a dilemma of how you’re getting things done: the declarative approach and the imperative approach. Many IaC tools lean toward one or the other for managing infrastructure resources, so the table below breaks down these two approaches:
| Declarative IaC Tool Approach: | Imperative IaC Tool Approach: | |
| Definition | Details the desired infrastructure state, such as configuration and resources. | Outlines the exact commands and steps needed to achieve the desired state of the infrastructure. |
| Ease of Use | The declarative approach defines what you need and how you need it, implying the process. | Needs a detailed instructions set, so the user must define how to achieve the desired state. |
| Execution | The tool performs and determines the actions needed to achieve the desired state. | Commands have to be executed in a specific sequence manually to achieve the desired state. |
| StateManagement | Simplifies resource teardown and updates by tracking the current state of the infrastructure. | The user is responsible for managing everything manually. |
| ChangeManagement | The changes are automatically deployed when the state is modified. | The user has to configure the changes manually. |
| Preferances | Most commonly used by the IaC tools due to its efficiency and automation capabilities. | Less common, but some specific scenarios require an imperative approach for greater control. |
These tools showcase the power of Infrastructure as Code, turning complex infrastructure tasks into manageable, repeatable processes.

IaC Practices – Managing Infrastructure Use Cases
To understand how IaC code really works, let’s look at its use cases for managing infrastructure. The table below compares the same configuration tasks with or without IaC infrastructure provisioning.
| With IaC: | Without IaC: | |
| Manual Configuration | Push the new server configuration to the control system. | Order hardware. Install the operating system. Set up a web server. Configure policies. |
| Server Testing | Set up the configuration code to the staging server and run stress and functionality tests. | Set up test environment. Deploy the web server. Run functionality tests. |
| Manual Set Up of Web Server | IaC tools automatically deploy the test configuration to the production environment. | Install the operating system. Set up the web server. Update the load balancer. Monitor for interruptions. |
| State Tracking and Changes | Utilize the version control system configurations to maintain a history of changes. | Use ticketing system objects. Manually update change logs. Inspect for potential errors. |
| Manual State Documentation | Provide the infrastructure with state files and up-to-date documentation. | Update the spreadsheet. Check for potential errors. Update metrics regularly. |
| Requirement Satisfaction | Define the new server in the infrastructure code. | Form a plan for manual integration of new data. |
These use cases show how Infrastructure as Code fits real-world demands, whether it’s dealing with a quick test environment or keeping a production system running. By leaning on consistent scripts and automation, operation teams can cut out the repetitive tasks and tackle everything with confidence.
Automate Manual Processes With ServerManina!
As a top-tier dedicated hosting and cloud provider, our AraCloud IaaS hosting solutions deliver what you need to manage your cloud infrastructure effortlessly. With our robust hosting solutions, you can forget the tedious tasks and let code handle the heavy lifting, keeping your systems smooth, secure, and ready for anything.
Quick Tip: If you’re a small organization looking for cloud solutions, automation, or configuration management, check out our cloud server guide for small businesses.
Infrastructure as Code – FAQs
What is Version Control in IaC?
Version control in IaC lets you track and manage changes to your infrastructure code, like using Git to keep everything organized and reversible. It’s a lifesaver for collaboration and fixing mistakes quickly.
What is Configuration Drift in IaC?
Typically, configuration drift appears when your infrastructure starts diverging from the code that’s supposed to define it, delivering server inconsistencies. Hence, over time, it can turn a tidy setup into a troubleshooting nightmare.
What is Hashicorp Configuration Language?
HashiCorp Configuration Language is a readable syntax that Terraform uses to write IaC scripts, making it easy to define your setup. It’s straightforward, without a learning curve, and excellent for newbies to adopt.
Was this page helpful?

