Hyper-V vs VMware: What’s the difference and which should you choose?

Hyper-V and VMware are both technologies that allow businesses and organizations to use a single computer or server for multiple applications and use cases. From the time it was released to the public till now, it has been in heavy use by many companies and individuals.
These technologies are both called server virtualization technologies and are a major part of IT and networking.
So, if you don’t know anything about these technologies or are confused about choosing the best one for your business, don’t worry. In this tutorial, we will cover what they are both used for and which one is better for your specific use case.
What is Server Virtualization?
If VMware and Hyper-V don’t ring a bell in your mind, you might be wondering what is server virtualization technology. But if you already have prior knowledge then you are free to skip this part.
Server virtualization is the practice of using virtualization software to partition a physical server into multiple isolated virtual environments, often referred to as a container. It allows you to run multiple virtual machines at a time.
Each container operates with its own distinct operating system also known as guest OS. These containers are completely isolated from each other, meaning that no virtual server can access the data from the other server. This is possible by making virtual disks for each VM (virtual machine).
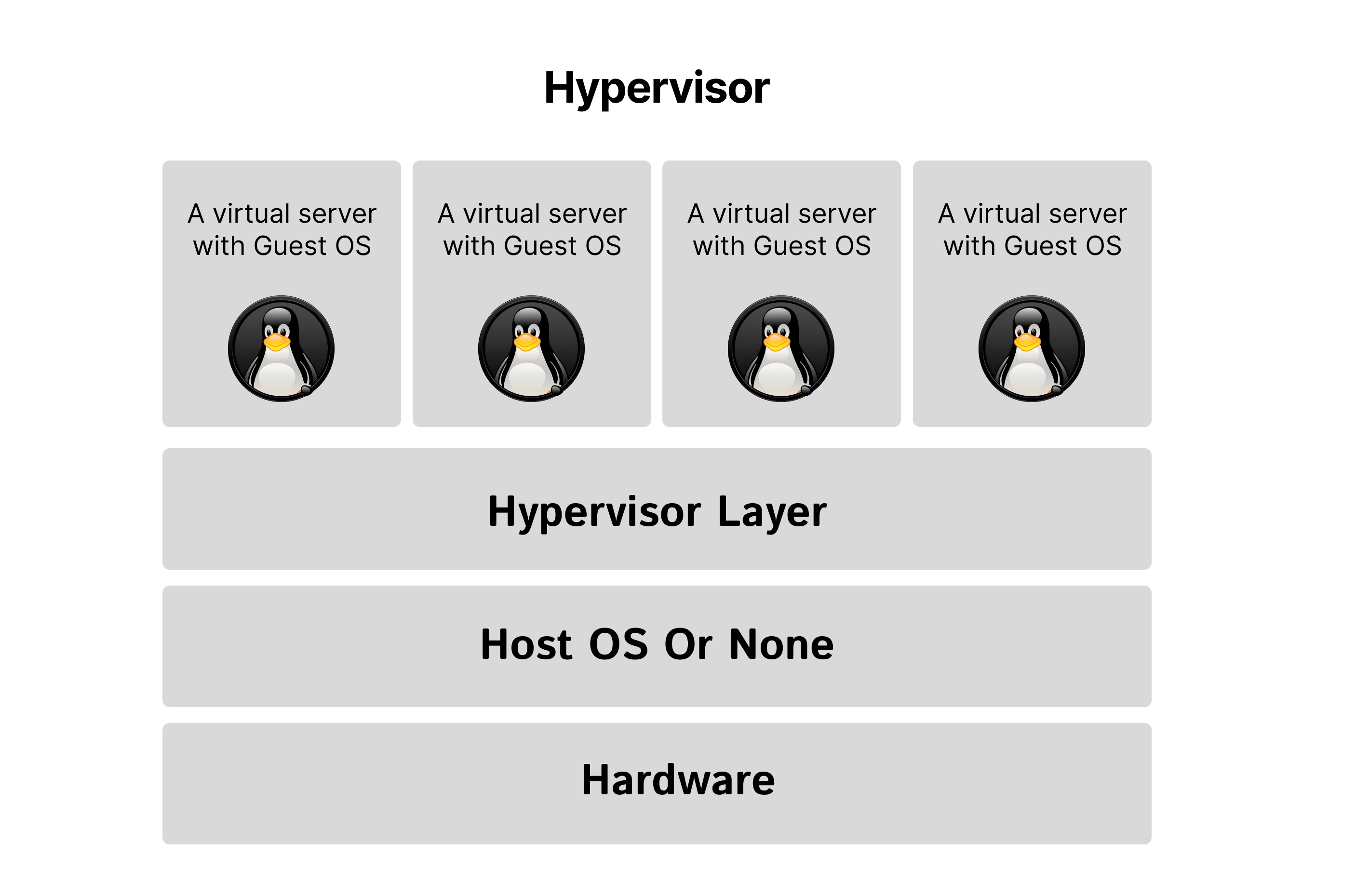
A Hypervisor is the real technology that enables the creation of a virtual machine and it sits between the hardware and the virtual machines.
Server virtualization is just a term used to describe the process of making virtual machines. However, the hypervisor is the real technology that is behind this process.
In the picture below you see a diagram of a hypervisor. Some hypervisors are installed on a host OS, which is called a Type-2 hypervisor. Others are installed directly on the hardware, which is called Type-1.
Benefits of Server Virtualization
The benefits of server virtualization are that it:
- Gets rid of extra IT costs and energy consumption
- Decreases the number of physical servers your company must have on its premises
- Creates an independent user environment
- Improves resource utilization
- Allows for dynamic resource allocation
- Offers improved resource prioritization
Learn more about Hyperconverged IaaS on the ServerMania Cloud.

VMware
This is the first type of server virtualization solution that is popular in the industry. VMware offers a range of virtualization solutions, with VMware-vSphere being their flagship product.
VMware VSphere is a cloud virtualization platform that is available for on-premise and cloud use. It uses VMware ESXi as its hypervisor.
VMware VSphere includes several components:
- VMware ESXi: VMware ESXi (formerly known as VMware ESX) is a Type-1 hypervisor that runs directly on bare metal (hardware) and does not require any Operating System. It is used in VSphere as a hypervisor and is responsible for running virtual machines and managing hardware such as memory, CPU, etc.
- VMware vCenter Server: This is a centralized management tool. It allows you to manage virtual machines or multiple ESXi hypervisors from a single interface.
Note! A complete guide to the VMware features comparison can be found here.
VMware VSphere System Requirements
Below are the system requirements of VMware ESXi hypervisor version 7.0.
CPU
- At least two CPU cores.
- Multi-core of 64-bit x86 processors.
- Requires the NX/XD bit to be enabled for the CPU in the BIOS.
Memory
- VMware VSphere requires a minimum of 8 GB of physical RAM to run virtual machines. But it is always recommended to increase it for better performance.
OS
- VMware ESXi could run almost all the major operating systems including Windows server, Mac OS server, and various kinds of Linux distributions.
Storage
- Requires a boot disk of at least 32 GB of persistent storage such as HDD, SSD, or NVMe
Note! VMware also offers a hardware compatibility tool, which will help determine if your hardware can run VMware.
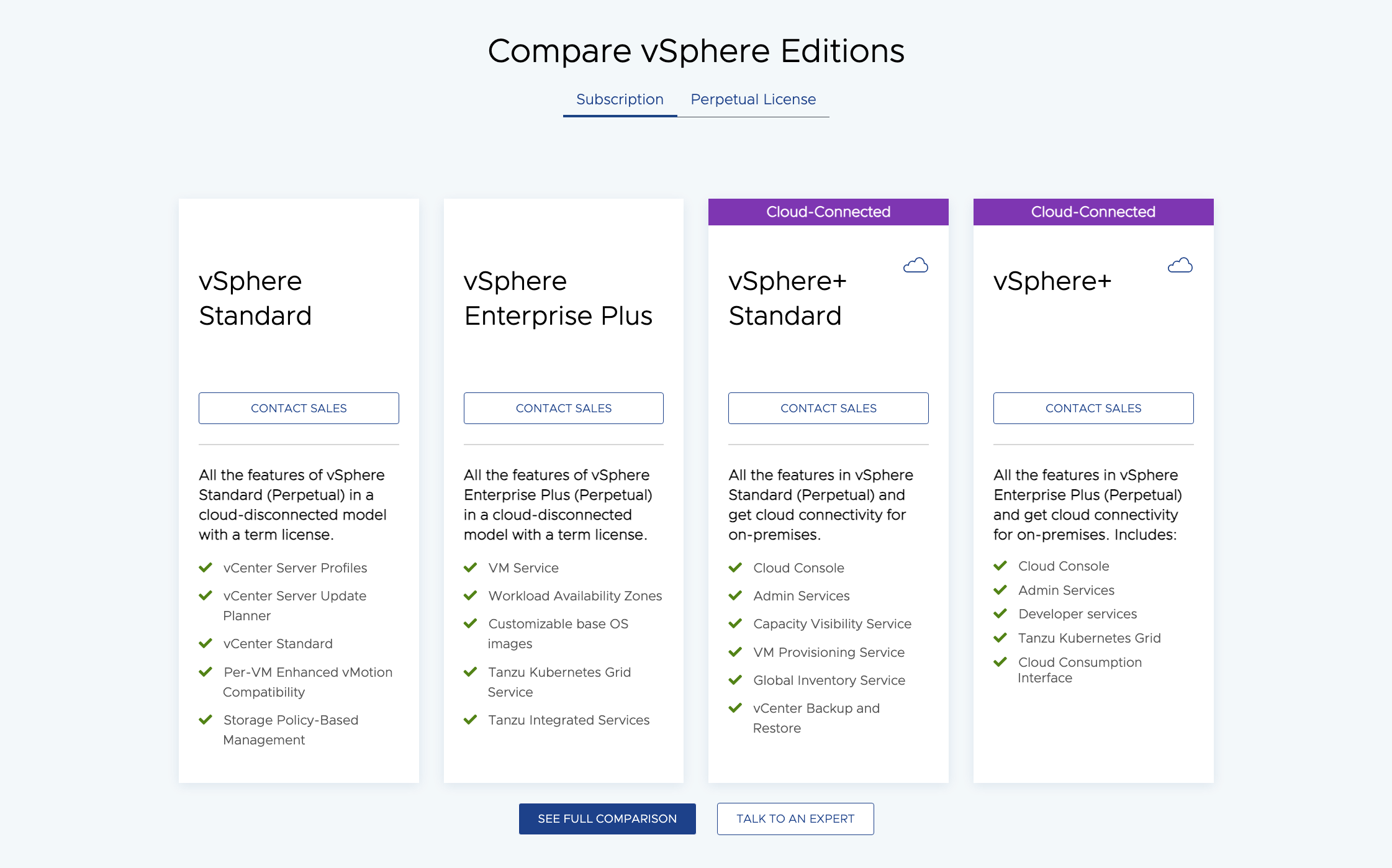
VMware Pricing
VMware pricing depends upon many different factors including license type, edition, and resources.
- Pricing typically depends on the number of CPUs or sockets in your physical servers. You’ll need to purchase licenses for each CPU.
- VMware also offers subscription-based licensing for vSphere, which provides more flexibility and may include access to additional features and services.
Below you can see a picture of VSphere editions:

Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a Type-1 Microsoft virtualization solution, designed for both Windows Server environments and Windows 10. In the new versions, it has also added support for the Linux operating system as well. Hyper-V could also be used on-premises or in the cloud using Microsoft Azure services.
Hyper-V System Requirements
Regardless of the specific Hyper-V features you plan to use, your system must meet these general requirements:
- A 64-bit processor with second-level address translation (SLAT) is necessary. This is needed to install the Hyper-V virtualization components, like the Windows hypervisor.
- VM Monitor Mode extensions are required.
- You should plan for at least 4 GB of RAM, although more memory is recommended.
- Virtualization support must be turned on in the BIOS or UEFI, including hardware-assisted virtualization (available in processors with Intel VT or AMD-V technology) and hardware-enforced Data Execution Prevention (DEP).
Hyper-V Pricing
Microsoft Hyper-V offers a range of editions with different pricing, spanning from $24.95 to $199 USD.
To determine the most suitable edition for your needs, explore the details and additional information about the product on their official website.
This will help you make an informed decision regarding which edition aligns best with your requirements. The available packages are mentioned below with their referring prices:
- Developer: $24.95 USD per month
- Bronze: $49 USD per month
- Silver: $89 USD per month
- Gold: $135 USD per month
- Platinum: $199 USD per month
Conclusion
Both VMware and Hyper-V have their pros and cons, so we’ve compared them below to help highlight the key differences.
Comparison in Pricing
The pricing for VMware and Hyper-V both depend on the resources you tend to use and the requirements of your business.
In essence, Hyper-V is considered to be an affordable alternative to VMware because VMware has various services that add to the overall cost of this solution.
Feature Comparison
To simplify the comparison of Hyper-V vs VMware, we have put together the following table:
| Hyper-V | VMWare |
|---|---|
| Hyper-V supports Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD operating systems. | VMware supports Windows, Linux, Unix and macOS operating systems. |
| Hyper-V’s pricing depends on the number of cores on the host and may be preferred by smaller companies. | VMware charges per processor and its pricing structure might appeal to larger organizations. |
| Hyper-V’s Cluster Shared Volume is somewhat more complex and more difficult to use than VMware’s storage deployment system. | VMware’s Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) holds a slight edge when it comes to clustering. |
| Hyper-V uses a single memory technique called “Dynamic Memory”. Using the dynamic memory settings, Hyper-V virtual machine memory can be added or released from the virtual machine back to the Hyper-V host. | VMware implements a variety of techniques, such as memory compression and transparent page sharing, to ensure that RAM use in the VM is optimized. It is a more complex system than Hyper-V’s memory technique. |
In Summary: Should You Choose Hyper-V or VMware?
When faced with the decision of choosing between Hyper-V and VMware, it becomes evident that your selection should be intricately tied to your specific hardware requirements and the overarching objectives of your business. The choice between these virtualization solutions is not a one-size-fits-all scenario; rather, it’s a nuanced decision that necessitates a thorough evaluation of several critical factors.
First and foremost, affordability plays a pivotal role in your decision-making process. Assessing your budget constraints and aligning them with the cost of licensing, hardware compatibility, and ongoing maintenance is imperative. It’s essential to strike a balance between your financial resources and the capabilities offered by each platform.
Furthermore, consider the essential features required to meet your operational needs. Does your business demand advanced features like seamless container migration, memory management tools for example VMware memory management techniques, or superior support for specific guest operating systems?
By carefully evaluating your essential feature set, you can ensure that the chosen virtualization solution aligns seamlessly with your business requirements. Additionally, take scalability into account, as your virtualization platform should have the capacity to grow alongside your evolving needs. Ultimately, the decision between Hyper-V and VMware should be a well-informed one, driven by a comprehensive understanding of your organization’s unique hardware, budget, feature, and scalability demands.
Next Step
In this guide, we’ve explained the difference between Hyper-V and VMware and have given you a better understanding of what they are used for.
If you would like to learn more about Hyper-V, take a look at Hyper-V Networking: what are the different switches used for? We also recommend taking a look at our Knowledge Base to see our latest articles and tutorial videos to help you with cloud server hosting and setup.
Need even more advice or would you like a custom quote? Book a server consultation with one of our experts. We will assist you in identifying the most suitable solutions for you or your business.
Was this page helpful?

