Managing and Monitoring Your Servers on AraCloud

Efficiently managing and monitoring your servers is crucial to maintaining optimal performance and ensuring your applications run smoothly. This guide will walk you through the tools and features AraCloud provides to help you manage and monitor your virtual servers with ease.
Checking Server Information and Performance
Stay informed about your server’s status and performance metrics:
- Click on Servers under the Quick Navigation menu or in the top bar menu
- Click on the server’s name you want to monitor
- Check the server’s usage and confirm the information is accurate
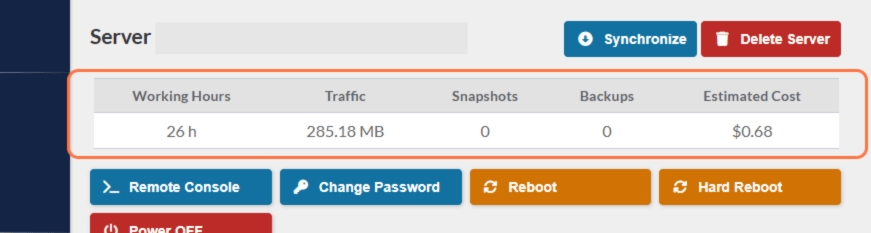
- Working Hours: The total time a server is operational and available for use.
- Traffic: The amount of data sent and received by the server.
- Snapshots: Number of point-in-time copies of the server’s state, including its data and configuration.
- Backups: Number of comprehensive copies of server data stored separately to ensure data can be restored in case of hardware failure, data corruption, or other disasters.
- Estimated Cost: The financial cost associated with running the server, including expenses for compute resources, storage, bandwidth, and any additional services.
Note: The working hours will get restarted every invoicing period.
- Check the Status window
- New: Server has been created but hasn’t been deployed
- Active: Server has been deployed
- Deactivated: Server has been deactivated due to overdue payment
- Banned: Server has been banned due to overdue payment
5. Check the State window
- Check the Volumes and Network Ports
Monitoring Tools
Keep an eye on your server’s performance with the monitoring tools provided by AraCloud.
- Click on “METRICS”
- Choose the time period you want to see the data from
- Navigate through the different charts
- CPU Time: This measures the amount of time the CPU spends processing instructions from applications and the operating system. It’s an indicator of how much processing power is being used.
- Memory Usage: This shows the amount of RAM being used by the server. High memory usage can indicate that applications are consuming a lot of resources, which might affect performance.
- Network Speed: This refers to the rate at which data is transmitted over the network. It’s usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- Network Packets: These are units of data sent over the network. Monitoring the number of packets can help understand the volume of network traffic.
- Network Drops: This metric indicates the number of packets that were lost or dropped during transmission. High network drops can signal network congestion or issues with network hardware.
- Disk Write: This measures the amount of data being written to the disk. High disk write activity can impact the performance of the server, especially if the disk is a bottleneck.
- Disk Read: This measures the amount of data being read from the disk. Similar to disk write, high disk read activity can affect server performance.
- Write Latency: This is the time it takes to write data to the disk. High write latency can indicate slow disk performance or issues with the storage system.
- Read Latency: This is the time it takes to read data from the disk. High read latency can also signal slow disk performance or storage system problems.
Accessing the Server’s Console
The server console is a powerful tool that allows direct interaction with the server’s operating system and hardware. It should be used with caution and only by authorized personnel.
What Can Be Done Using the Console:
- System Management: Perform administrative tasks such as starting, stopping, and configuring services.
- Software Installation and Updates: Install new software, apply updates, and manage existing applications.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose and resolve system issues, monitor system performance, and review logs.
- User Management: Add, remove, and manage user accounts and permissions.
- File Management: Access, modify, and manage files and directories on the server.
Who Should Use the Console:
- Authorized Personnel Only: Access to the server console should be restricted to system administrators and IT professionals who have the necessary knowledge and permissions.
- Trained Users: Only individuals who have received proper training and understand the potential risks and impacts of their actions should use the console.
- Supervised Access: In some cases, less experienced users may be granted access under the supervision of a qualified administrator.
Warning: Unauthorized or improper use of the server console can lead to system instability, data loss, and security vulnerabilities. Always ensure that you have the appropriate permissions and knowledge before performing any actions on the server console.
- Click on the server’s name you want to access the console
- Click on Remote Console
- The console will open on a new window
Changing Server’s Password
- Click on the server’s name you want to change the password from
- Click on Change Password
- Enter new password and confirm
- Click on OK to save the changes
Rebooting Server
- Click on the server’s name
- Choose between “Reboot” or “Hard Reboot” options
- Soft Reboot: Use this method for routine maintenance, software updates, and troubleshooting minor issues. It’s the preferred method for most situations as it’s safer for your data and system integrity.
- Hard Reboot: Use this method only when the server is unresponsive or frozen, and a soft reboot is not possible. It’s a last resort due to the higher risk of data loss and system damage.
- Verify the state and if the information is correct
- Once the reboot is complete, the server’s state should change to active, which means the reboot has been completed
Powering Off a Server
Powering off a server is sometimes necessary for several important reasons:
- Software Updates: Some software updates, especially those involving the operating system or critical applications, may require a reboot to complete the installation.
- Troubleshooting: If a server is experiencing issues, a reboot can sometimes resolve problems by resetting the system.
- Energy Savings: In some cases, servers that are not in use can be powered down to save energy and reduce costs.
- Click on the server’s name you want to power off
- Click on “Power OFF”
- Click on OK to save the changes
- Confirm the server has been successfully powered off by checking the STATE
5. To continue using the server, click on “Power ON” and the usage will be resumed
6. Use the Reset State button only if there is a mismatch between the server state and the console state. I.e. Server was turned down using the console and is still showing up as powered on in the portal
Deleting a Server
- Click on the server’s name you want to delete
- Click on “Delete Server”
- Click on OK to save the changes
Synchronizing a Server
- Click on the server’s name you want to synchronize
- Click on “Synchronize”
- Confirm the last updated date is match the time you synchronized the server
Creating a Volume Snapshot
Creating a volume snapshot in AraCloud is a crucial process for ensuring data integrity and availability. Volume snapshots allow you to capture the state of your data at a specific point in time, providing a reliable backup that can be used for data recovery.
- Click on Servers
- Click on cloud-server
- Click on VOLUMES
- Click on Take Snapshot
Resizing a Server
Resizing a server in AraCloud is an essential task for optimizing resource allocation and ensuring your applications run efficiently. Whether you need to scale up to handle increased workloads, resizing a server allows you to adjust the computing resources to match your current needs.
- Select the server that you want to resize
- Click on Resize Server
- You can resize the CPU count, RAM, or disk using the sliders
- If the options provided are still limited turn on the Request More Resources option
The resize request will be created for revising. It will be Accepted or Declined as soon as the admin takes a look at it.
- Click on OK
Next Steps
- Review Billing Information: Visit the Billing section to track usage costs and manage payment methods.
- Update Account Settings: Explore the Settings section to customize user roles and permissions.
Need Assistance?
If you encounter any issues, visit our Troubleshooting page or contact our support team by creating a ticket.
Was this page helpful?

